Understanding Modular and Manufactured Homes: A Code Comparison
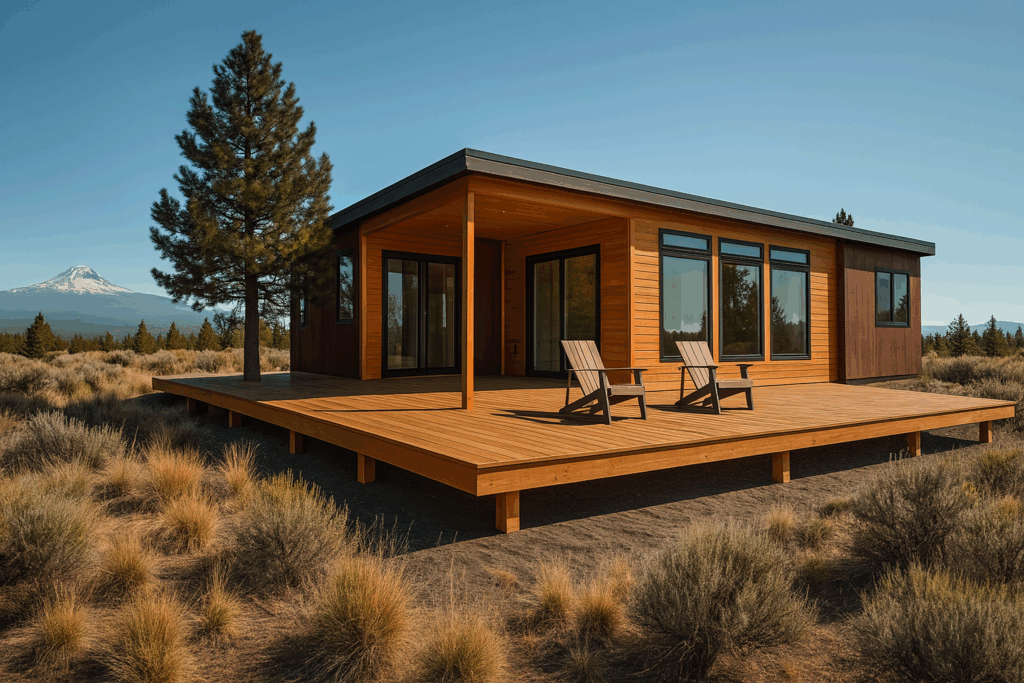
This article clarifies the differences between prefab, modular, and manufactured homes, explaining how modular construction combines factory precision with the permanence and quality of site-built houses. It highlights advantages such as faster timelines, eco-conscious practices, design flexibility, and financial benefits while addressing common misconceptions.
What you’ll learn:
- The difference between prefab, modular, and manufactured homes
- Why modular homes meet and exceed IRC building codes
- Quality materials, efficient processes, and reduced waste
- Faster build times compared to traditional construction
- Eco-conscious features and healthier indoor air quality
The world of homebuilding has shifted dramatically in recent years. Homeowners are no longer limited to traditional site-built construction. Instead, factory-built options have emerged as a sustainable, efficient and design-forward alternative. As a result, the terms “prefab” and “modular” are often used interchangeably, which can cause confusion.
Are they the same thing? Are modular homes simply another name for prefab? And how do manufactured homes fit into the picture?
Understanding these differences matters. At ideabox, we specialize in modular homes, which are a type of prefab construction. Knowing how prefab, modular and manufactured homes compare will give you the clarity you need as you consider your options.
What Is a Prefab Home?
Prefab is short for prefabricated. It refers to any home built in a factory setting before being transported to its final site. Under this umbrella category, there are two main types: manufactured homes and modular homes.
- Manufactured homes are built to federal HUD standards. They do not require a permanent foundation and are not constructed to local building codes. They are sometimes called mobile homes.
- Modular homes are built to the same International Residential Code (IRC) as site-built homes. They require a permanent foundation, undergo the same inspections, and meet the same safety and quality standards as any home in your neighborhood.
This distinction is critical. All modular homes are prefab, but not all prefab homes are modular.
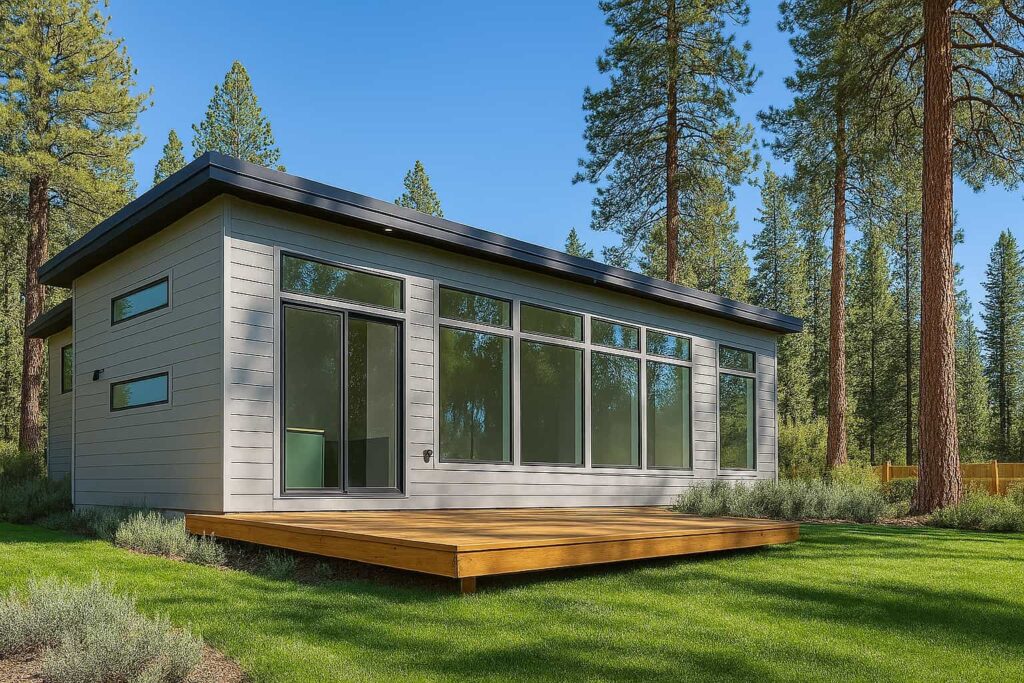
Why Modular Homes Stand Out
Choosing a modular home means choosing a residence that combines the precision of factory construction with the permanence and quality of traditional building. There are several advantages that make modular homes a smart choice.
Quality Materials and Minimal Waste
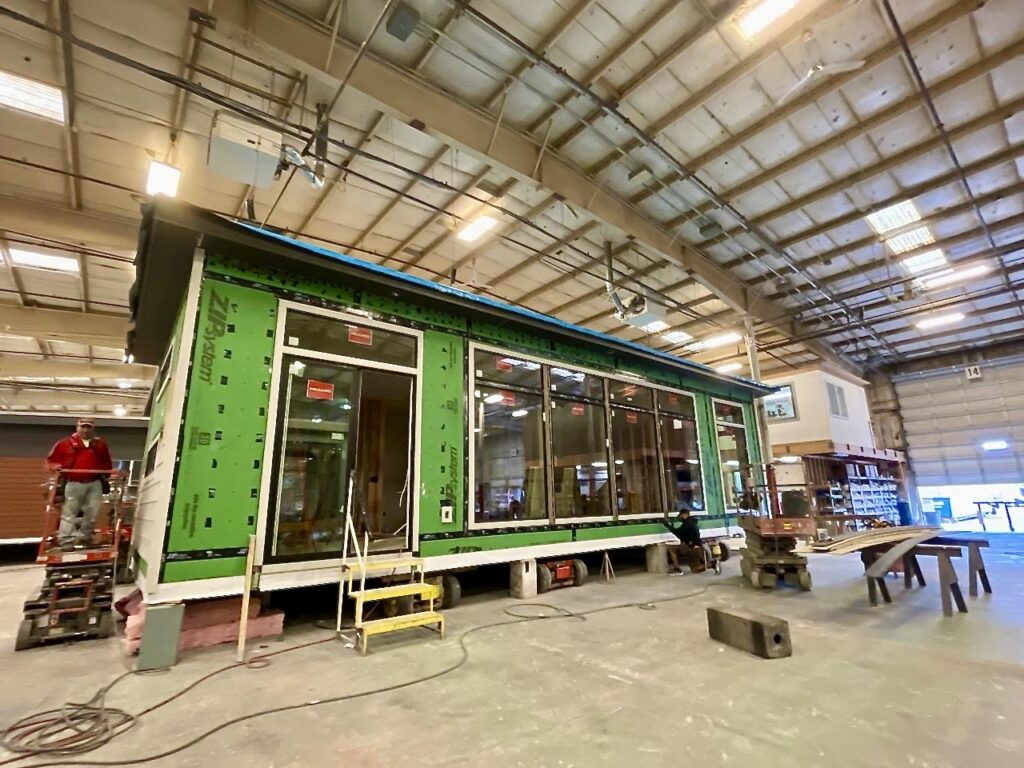
Modular homes are built with the same, and often superior, materials as site-built homes. At ideabox, 2×6 exterior walls are standard, providing strength, durability and enhanced insulation. Because construction takes place in a controlled environment, materials are protected from weather damage, which eliminates common issues like warped wood or moisture exposure.
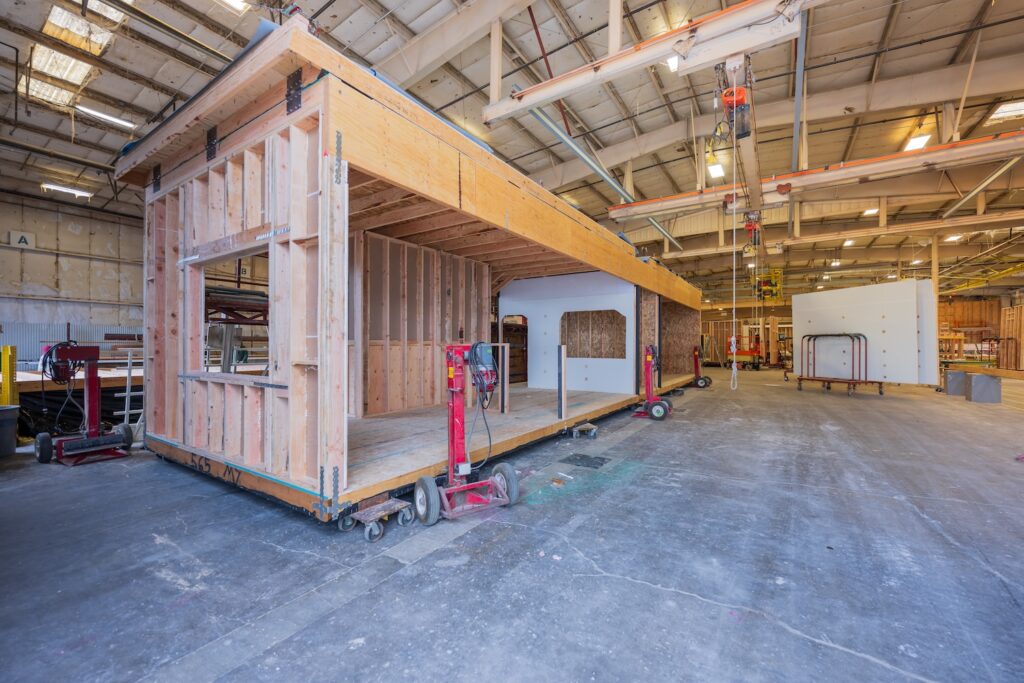

Another major benefit of factory construction is efficiency. Every cut and assembly is precise, which results in very little material waste. This makes modular homes not only strong and durable but also more environmentally responsible.
Faster Build Times
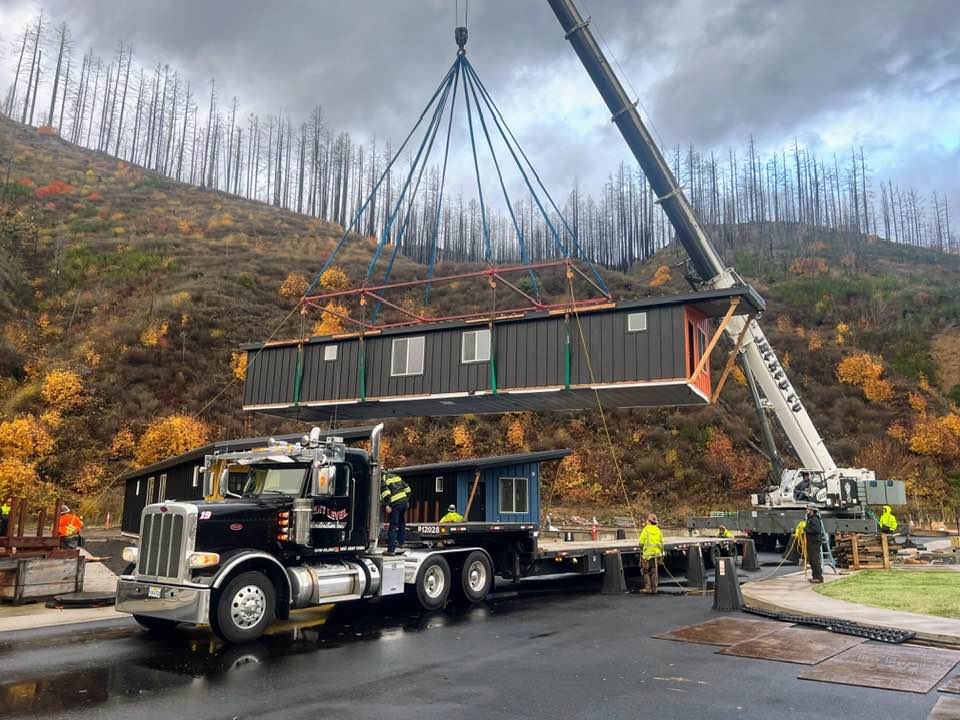
Time is one of the greatest advantages of modular construction. Traditional homebuilding can stretch over a year or more, with delays caused by weather, labor shortages or supply chain disruptions. Modular homes, on the other hand, can often be completed in an average of eight months.
While your home is being built in the factory, site preparation is happening at the same time. By the time the modules are delivered, the foundation and utilities are ready, allowing for a smooth installation process. This overlap shortens the overall project timeline and helps homeowners move in sooner.
Eco-Conscious Choices
Sustainability plays an important role in modern housing, and modular homes are designed with eco-conscious practices in mind. Many of the materials used in modular homes have recycled content and are selected for their durability and fire-resistant qualities.
Indoor air quality is also prioritized. Modular homes are equipped with fresh air returns to encourage healthy circulation. Energy-efficient insulation, high-performing windows and thoughtful building practices reduce energy use and lower monthly utility costs.
For homeowners who care about their environmental footprint, modular homes offer a healthier and more sustainable way to live.
Financial Benefits
Modular homes provide long-term value in several ways. The efficiency of the building process reduces hidden costs and avoids many of the delays associated with site-built homes. Materials are used more effectively, which lowers waste and helps keep budgets under control. Loans are available through most banks for Modular homes, similar to a typical conventional home loan.
Energy-efficient features also reduce ongoing expenses. Highly rated U-factor windows ensure heat stays inside during the colder months and cool air is preserved during the summer. Over time, these design details translate into significant savings on utility bills.
Modular vs. Manufactured: Clearing Up the Confusion
One of the most common misconceptions is that modular homes and manufactured homes are the same thing. While both fall under the prefab category, they differ in critical ways.
Modular homes are built to the same IRC codes as any other house on your street. They are installed on a permanent foundation, use high-quality materials, and hold their value much like traditional homes.
Manufactured homes, by contrast, are built to HUD codes and do not require a permanent foundation. They are not subject to the same local inspections or building standards. While they remain a housing option, they are very different from modular homes in terms of quality, durability and resale value.
Understanding this distinction helps homeowners feel confident in choosing modular construction, knowing that it represents a permanent, high-quality solution.
Design Flexibility
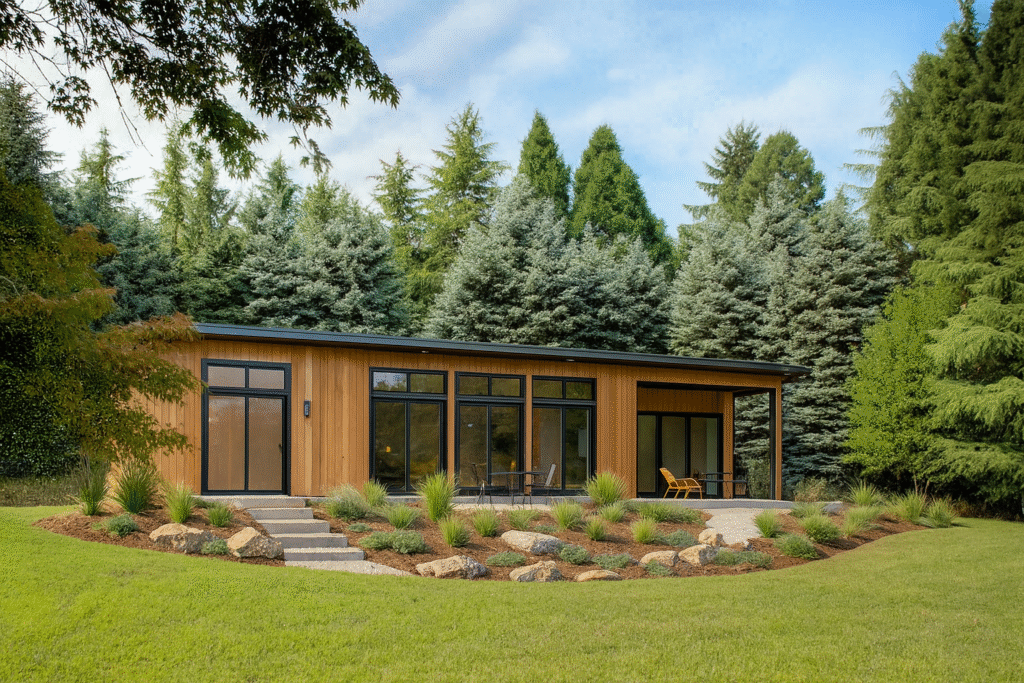
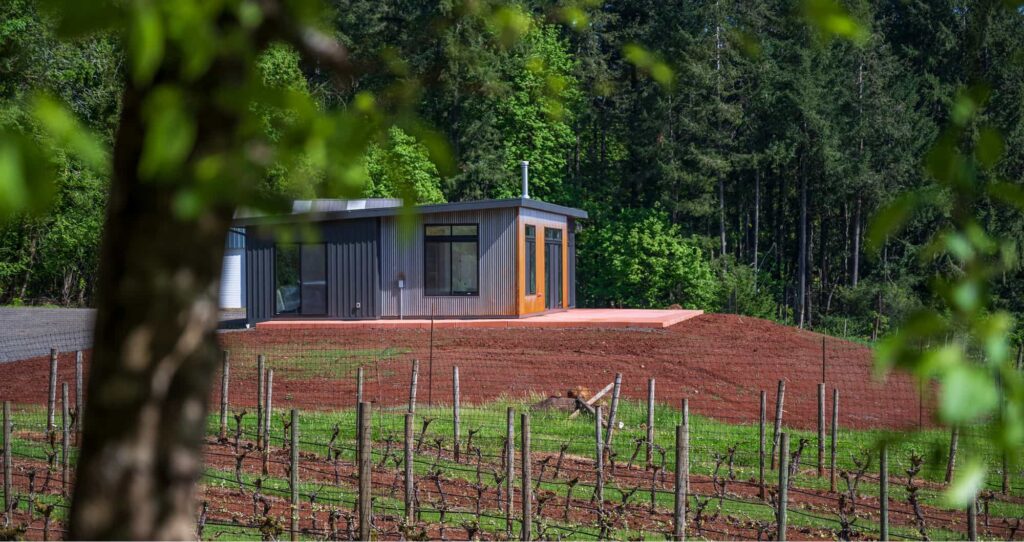
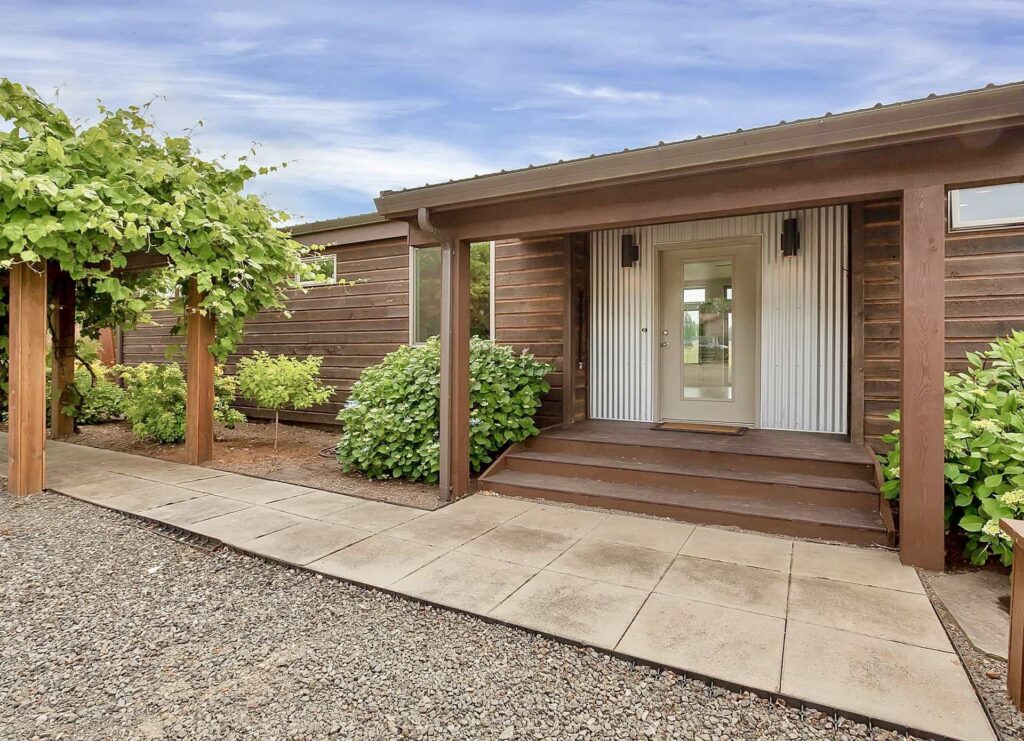
A common assumption is that prefab or modular homes are limited in design, leaving buyers with cookie-cutter layouts. In reality, modular homes are highly flexible and can be tailored to reflect the way you want to live.
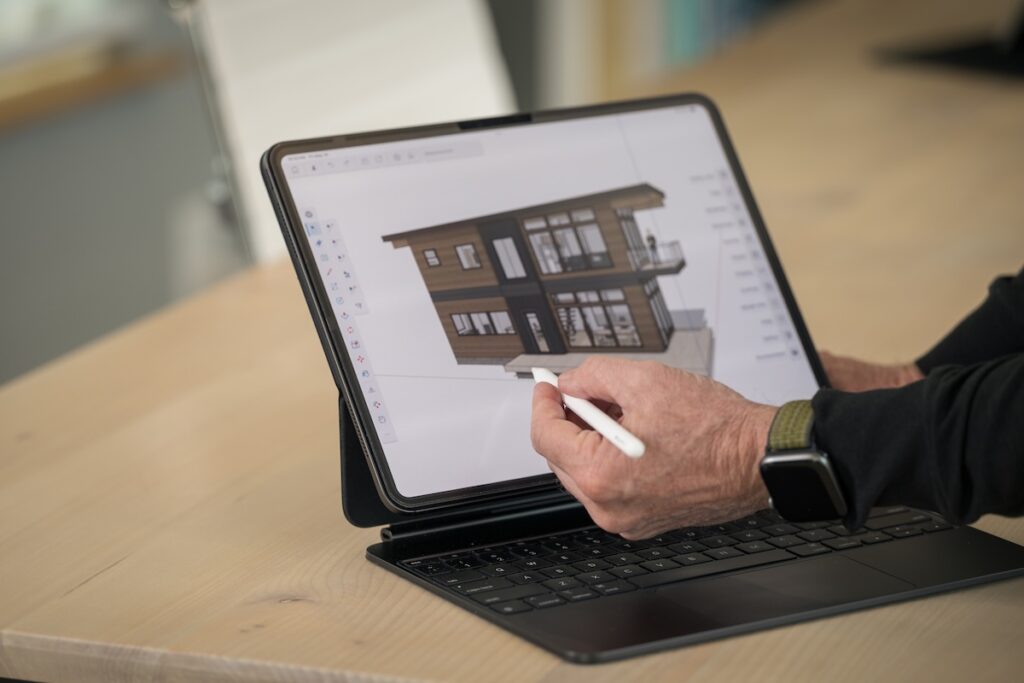

At ideabox, homeowners can start by exploring thoughtfully crafted models and from there, details such as layout adjustments, finishes and design features can be customized. Whether you prioritize open spaces, built-in storage, or natural light, modular homes adapt to your needs and lifestyle.
Still Have Questions?
Buying a home is one of the most important decisions you will make, and it is natural to have questions. To help, we have put together a dedicated FAQ page where you can find answers to many of the most common inquiries about prefab and modular homes.
You can also browse our Blog page for insights on sustainability, design and energy efficiency. Both previously published articles and upcoming ones aim to provide deeper dives into topics you may be curious about.
And if you cannot find the information you need, we are always happy to talk. Feel free to reach out directly and we will help guide you through the process.
Final Thoughts
Prefab homes are a broad category that includes both modular and manufactured construction. Modular homes stand out within that category as permanent, high-quality residences built to the same standards as site-built houses. They combine efficiency, sustainability and design flexibility in ways that traditional construction often cannot match.
At ideabox, we specialize in modular homes that reflect modern living. With faster timelines, eco-conscious materials, smart budget advantages and flexible design, modular construction is not just a trend but the future of housing.
If you are ready to take the next step, begin by learning what makes our approach unique. Your dream home may be closer than you think.
Frequently Asked Questions About Understanding Modular and Manufactured Homes
“Prefab” means factory-built. Under that umbrella are manufactured homes (built to federal HUD standards, no permanent foundation) and modular homes (built to IRC codes like site-built houses and set on a permanent foundation). All modular homes are prefab, but not all prefab homes are modular.
Yes. Modular homes are constructed to the International Residential Code (IRC), require a permanent foundation, and undergo the same inspections and safety/quality standards as any home in your neighborhood.
Modules are built in a climate-controlled environment, so materials aren’t exposed to rain or moisture. With precise cuts and assembly, waste is minimized and quality is consistent. (At ideabox, 2×6 exterior walls are standard for strength, durability, and insulation.)
Modular construction often finishes in about eight months. While the home is built in the factory, site prep and foundation work happen in parallel, which shortens the overall timeline.
Expect energy-efficient insulation, high-performing/U-factor windows, and fresh air returns for better indoor air quality. Thoughtful, tight construction helps reduce energy use and can lower monthly utility costs.
Yes on both. Loans are available through most banks for modular homes, similar to conventional mortgages. And design is highly flexible: start from a crafted model, then tailor layouts, finishes, and features to match how you want to live.

Let’s Build Something Great Together
Whether you’re ready to start planning or just want to explore options, we’re here to help. Let’s talk about your future home today.











